SQL Server – Understanding of SQL Server Role and Database Role
SQL Server supports the two authentication mode as Windows authentication mode and Mixed authentication mode. Once the user is authenticated, SQL server will allow access to the user based on the permission that user has. All the user permissions are based on Server Role and Database Role. So let try to user understand the meaning of each server role and database role.
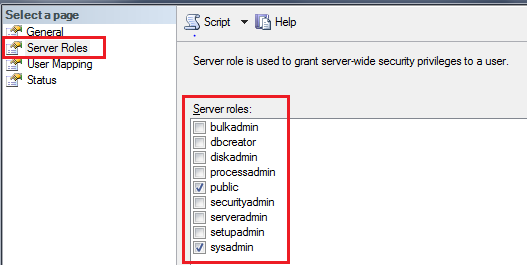
Server Role:
| Role Name | Permission user can have |
| bulkadmin | Can run the BULK INSERT statement. |
| dbcreator | Can create, alter, drop, and restore any database. |
| diskadmin | Can managing disk files. |
| processadmin | Can end processes that are running in an instance of SQL Server. |
| public | Default role assigned to each login. |
| securityadmin | Can manage logins and their properties. |
| serveradmin | Can change server-wide configuration options and shut down the server. |
| setupadmin | Can add and remove linked servers by using Transact-SQL statements. |
| sysadmin | Can perform any activity in the server. |
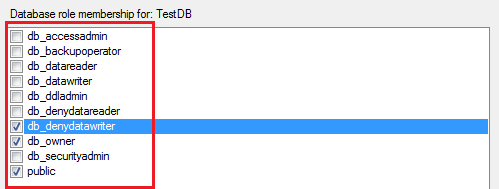
Database Role
| Role Name | Permission user has |
| db_accessadmin | Alter any users, create schema, connect |
| db_backupoperator | Back up database, log, and create checkpoint |
| db_datareader | Can execute select statement |
| db_datawriter | Can execute delete, insert, and update statements |
| db_ddladmin | alter—assembly, asymmetric key, certificate, database DDL trigger, database event, notification, dataspace, fulltext catalog, message type, remote server binding, route, schema, service, symmetric key, checkpoint; create—aggregate, default, function, procedure, queue, rule, synonym, table, table, view, XML schema collection and references |
| db_denydatareader | Cannot execute select. |
| db_denydatawriter | The role is to revoke the right/permission for select statement The role is to revoke the right/permission for select statement. |
| db_owner | Can perform any action in the database |
| db_securityadmin | Can alter—application role, any role, create schema, view definition |
| dbm_monitor | Can view most recent status in database mirroring monitor |